
The Second Biology Section is responsible for research and casework concerning anthropological materials such as bones, teeth, and facial images of living persons. Its research activities are mainly directed toward the personal identification of unknown skeletal remains and living persons in criminal cases, especially using skull/face superimposition, facial reconstruction from the skull, radiographic comparison, and physiognomic comparison between the criminal and the suspect. Furthermore, advanced research for estimating sex, age, and the time since death of skeletal remains is also carried out.
Personal identification of Unknown Skeletal Remains
-Computer-assisted Superimposition Technique-
In identifying unknown skeletal remains, a skull/face superimposition technique is performed. The contours, soft tissue thickness and anatomical relationships on the superimposition image are examined to judge whether or not the unknown skull is the presumed person. A computer-assisted superimposition system for improving the accuracy and speed identification was developed by NRIPS.
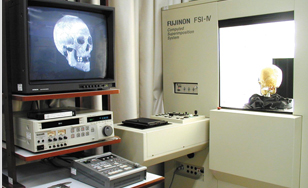
Computer-assisted superimposition system.
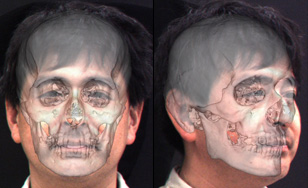
Superimposition image of a skull and facial photo.
Facial Identification of Living Persons
-Physiognomic Comparison using a 3D Range Finder-
For the identification of criminals captured by a surveillance camera or TV, NRIPS developed a new computer-assisted physiognomic comparison system using a 3D range finder. This system enabled us to exactly assess the results of a morphological comparison, anthropometrical analysis, and reciprocal point matching between the two facial images of the criminal and the suspect at the same facial orientation.

Physiognomic comparison system using a 3D range finder.
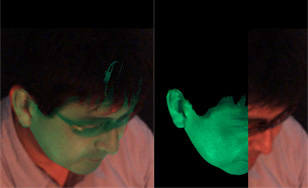
2D and 3D facial image superimposition.
