About JAFIC
1 Principal Role of JAFIC
JAFIC was established within the Organized Crime Department, the Criminal Investigation Bureau of the National Police Agency on 1st April 2007, when the Act on Prevention of Transfer of Criminal Proceeds came into force. JAFIC is an institution playing a central role in the enforcement of the said law mainly by collecting, arranging and analyzing suspicious transaction reports (STRs) filed by specified business operators and disseminating such information to public prosecutors etc.
2 Background of Establishment of JAFIC
Many countries have institutions equivalent to JAFIC. They are called FIUs. Egmont Group,established in 1995 as a forum for exchanging information between FIUs, defines an FIU as a "central, national agency responsible for receiving, analyzing and disseminating to the competent authorities, disclosures of financial information: (1)concerning suspected proceeds of crime and potential financing of terrorism, or (2)required by national legislation or regulation, in order to combat money laundering and terrorism financing".
In Japan, report of suspicious transactions was made obligatory for the first time by the Anti-Drug Special Provisions Law, which came into effect in July 1992, but it did not establish the system for centralization and dissemination of the information. Japan's first FIU was established within the Financial Supervisory Agency (reorganized into the Financial Services Agency in July 2000), when the Act on Punishment of Organized Crimes came into effect in February 2000, and it had the responsibility to handle information on suspicious transactions and exchange information with foreign counterparts under this Act.
The Act on Prevention of Transfer of Money Laundering, which was adopted in 2007, would expand the reach of reporting entities from financial institutions etc. to those and non financial institutions such as real estate agents and dealers in precious metals and stones, and the scope of suspicious transaction reports would accordingly be expanded as well. Therefore, it was thought that the National Police Agency, which can make the most of reported information for investigation or countermeasures against organized crime and terrorism, is more suited than the Financial Service Agency, which supervises only financial institutions, for the new role of Japan FIU that deals with the expanded STRs. This idea was unveiled in November 2005, when Government's "Headquarters for the Promotion of Measures against Transnational Organized Crime and Other Relative Issues and International Terrorism" decided to draft the bill of the new AML/CFT law.
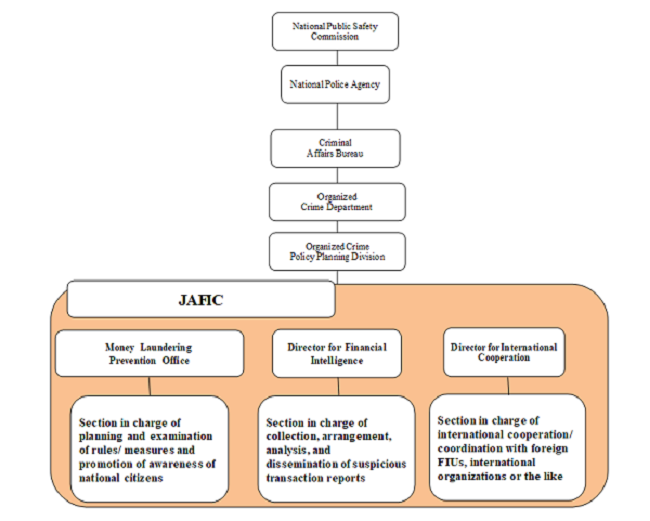
The Act on Prevention of Transfer of Criminal Proceeds has made it clear that the National Public Safety Commission (NPSC), which controls the National Police Agency and is aided by it, is responsible for prompt and appropriate collection, arrangement and analysis of suspicious transaction reports filed from specified business operators. The Act has also granted the NPSC a function related to the handling of STRs including their dissemination to foreign FIUs as well as a function concerning complementary supervisory measures against specified business operators. JAFIC has been established within the Organized Crime Department, the Criminal Investigation Bureau of the National Police Agency, as a new Japan's FIU to perform these functions.
3 Mission and Structure
JAFIC is in charge of the following tasks provided in the Act on Prevention of Transfer of Criminal Proceeds:
- - Collection, arrangement, analysis and dissemination of information on suspicious transactions to investigative authorities etc.
- - Dissemination of information to foreign FIUs;
- - Provision of information and complement of supervisory measures by administrative authorities to ensure that specified business operators take required measures;
JAFIC also plans and examines the legal system related to AML/CFT and various measures such as "the Guideline for Promotion of the Criminal Proceeds Control" etc. It also participates in the discussion of international standards related to AML measures.
The structure of JAFIC is illustrated in the chart below. It is currently composed of about 90 people under the Director for Prevention of Money Laundering.